Table of Contents
Ulcerative Colitis: Symptoms, Causes & Effective Management
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) characterized by persistent inflammation and ulcers primarily affecting the lining of the colon and rectum. This inflammation can lead to discomfort, frequent bowel movements, and significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and overall health.
Quick Facts
- Prevalence: Affects approximately 0.2% of the global population.
- Common Symptoms: Diarrhea, abdominal pain, rectal bleeding.
- Affected Population: Often diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 35, equally affecting men and women.
Understanding Ulcerative Colitis
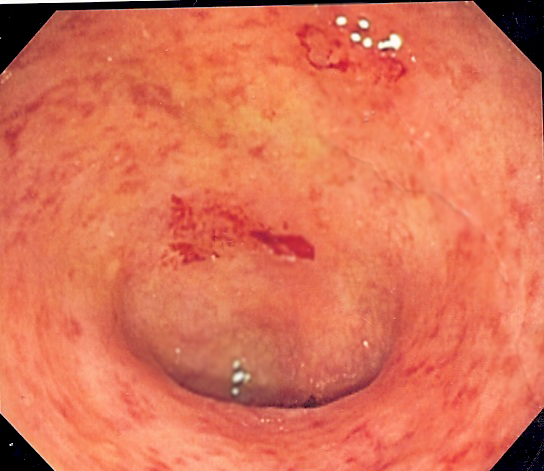
Ulcerative colitis involves chronic inflammation of the colon’s innermost lining, leading to ulcers and irritation. Unlike Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis typically affects a continuous section of the colon, beginning from the rectum and potentially extending upward, causing persistent symptoms and potential complications.
Common Symptoms
Early recognition and effective management of symptoms can greatly enhance quality of life. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent diarrhea, often containing blood or mucus
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Urgent need to have bowel movements
- Rectal bleeding and discomfort
- Fatigue and reduced appetite
- Unintended weight loss
- Anemia due to chronic blood loss
- Fever and dehydration during severe flare-ups
Symptoms often fluctuate between periods of remission and flare-ups, varying in intensity and frequency among individuals.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of ulcerative colitis remains unknown, multiple factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Genetics: Having a family history of IBD significantly increases risk.
- Immune System Dysfunction: An abnormal immune response triggers chronic inflammation in the colon.
- Environmental Factors: Diet, stress, exposure to certain infections, and use of certain medications can exacerbate symptoms or trigger flare-ups.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing ulcerative colitis typically involves several key approaches:
- Medical History: Comprehensive review of symptoms, family medical history, and lifestyle factors.
- Physical Examination: Evaluation for abdominal pain, tenderness, and signs of malnutrition or anemia.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests for inflammation, anemia, electrolyte imbalances, and stool tests to exclude infections.
- Imaging and Endoscopy: Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy to directly visualize the colon lining, assess inflammation severity, and take tissue biopsies for definitive diagnosis.
Effective Treatments and Management
Managing ulcerative colitis involves controlling inflammation, alleviating symptoms, and preventing complications:
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs (aminosalicylates), corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologic therapies targeting inflammation pathways.
- Dietary Adjustments: Personalized nutritional strategies to manage symptoms and maintain nutritional health, potentially involving avoidance of trigger foods.
- Lifestyle Changes: Stress management techniques, regular moderate exercise, maintaining adequate hydration, and avoiding tobacco and alcohol.
- Surgical Intervention: Surgery may be necessary to remove severely affected portions of the colon or address complications, significantly improving quality of life in some cases.
Potential Complications if Left Untreated
Without proper management, ulcerative colitis can result in significant complications:
- Severe dehydration and nutritional deficiencies
- Increased risk of colon cancer, especially with prolonged inflammation
- Perforation or severe bleeding from colon ulcers
- Toxic megacolon, a life-threatening condition where the colon rapidly expands
- Increased susceptibility to infections due to compromised intestinal health
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience persistent diarrhea, rectal bleeding, severe abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, or significant changes in bowel habits. Early intervention and treatment significantly improve outcomes and prevent complications.
Practical Tips for Living with Ulcerative Colitis
Effective daily management strategies include:
- Strict adherence to medication schedules and attending regular medical appointments.
- Maintaining a balanced diet tailored to individual needs to control symptoms.
- Staying well-hydrated and replenishing electrolytes during flare-ups.
- Practicing stress management and relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness.
- Participating in support groups to connect with others, exchange experiences, and gain emotional and practical support.
Recent Research and Advances
Current research continues to advance understanding and treatment of ulcerative colitis:
- Development of novel biologic therapies targeting specific inflammatory processes.
- Studies examining the role of gut microbiota and probiotics in managing symptoms.
- Advances in minimally invasive surgical techniques and post-operative care, improving recovery outcomes.
- Exploration of genetic and environmental factors contributing to disease onset and progression.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is ulcerative colitis curable? Currently, there is no cure, but effective treatments can manage symptoms, maintain remission, and significantly improve quality of life.
Can diet alone control ulcerative colitis symptoms? Diet plays a crucial role in symptom management and overall health, but typically medication is also necessary to control inflammation effectively.
Is ulcerative colitis hereditary? Genetics can significantly influence risk, and having a family member with IBD increases the likelihood of developing ulcerative colitis.
Additional Content
For comprehensive information on the various treatments you can explore our Autoimmune Disease Treatment page. If you are seeking expert medical advice, our Top Autoimmune Doctors section provides a list of highly recommended specialists. Additionally, for an overview of other autoimmune conditions, visit our Autoimmune Diseases page.