Table of Contents
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Symptoms, Causes & Effective Management
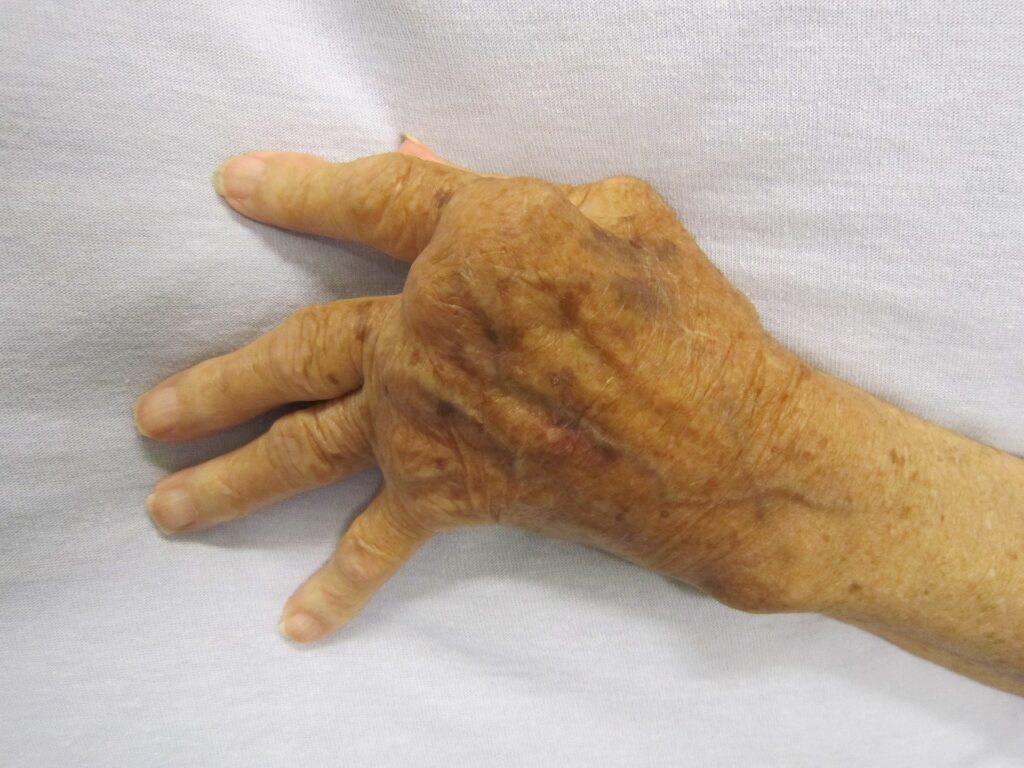
This is a chronic autoimmune disease primarily affecting joints, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling. RA significantly impacts mobility, quality of life, and overall well-being.
Quick Facts
- Prevalence: Affects approximately 1% of the global population.
- Common Symptoms: Joint pain, stiffness, swelling.
- Affected Population: Typically begins between ages 30-60, more common in women, but it can occur at any age.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
This disease develops when your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, causing chronic inflammation. If untreated, it can lead to permanent joint damage and disability.
Common Symptoms
Identifying symptoms early is key for effective management:
- Painful, swollen joints, often symmetrical
- Joint stiffness, particularly in the mornings lasting over 30 minutes
- Fatigue, fever, and weight loss during flare-ups
- Warmth and redness around affected joints
- Reduced joint mobility and function
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of this autoimmune condition remains unknown, several factors can increase your risk:
- Genetics: Family history of autoimmune diseases.
- Gender: Women are significantly more affected.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking increases risk and severity.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain infections or pollutants.
- Obesity: Associated with increased risk of developing RA.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History: Reviewing symptoms, family history, and lifestyle factors.
- Physical Examination: Assessing joint swelling, tenderness, and mobility.
- Blood Tests: Checking for inflammation (CRP, ESR) and antibodies (rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP).
- Imaging Tests: X-rays or MRIs to evaluate joint damage and inflammation.
Effective Treatments and Management
Effective management strategies aim to control inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and prevent joint damage:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics.
- Physical Therapy: Customized exercise plans to maintain joint function, strength, and mobility.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Balanced nutrition, regular exercise, adequate rest, and stress management.
Potential Complications if Left Untreated
Untreated RA can lead to severe complications:
- Progressive joint damage and disability
- Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Osteoporosis and higher fracture risk
- Lung inflammation and scarring
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if experiencing persistent joint pain, swelling, or stiffness, particularly if symptoms interfere with your daily activities or worsen over time. Early diagnosis significantly improves outcomes.
Practical Tips for Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Effective daily management includes:
- Consistent adherence to prescribed medications and treatments.
- Regular low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or yoga.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress.
- Employing assistive devices or modifications at home to ease tasks.
- Connecting with RA support groups for emotional and practical support.
Recent Research and Advances
Recent advancements offer improved treatment options:
- Development of targeted biologic therapies addressing specific inflammatory pathways.
- Advances in early diagnosis through improved imaging and biomarkers.
- Research into personalized treatment approaches tailored to individual symptoms and disease progression.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is rheumatoid arthritis curable? Currently, RA has no cure, but symptoms and progression can be effectively managed through appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Can diet impact RA symptoms? Yes, a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce symptoms and support overall joint health.
Does rheumatoid arthritis only affect joints? Primarily, RA affects joints, but it can also impact other organs such as the lungs, heart, and eyes, leading to additional health issues.
Additional Content
For comprehensive information on the various treatments you can explore our Autoimmune Disease Treatment page. If you are seeking expert medical advice, our Top Autoimmune Doctors section provides a list of highly recommended specialists. Additionally, for an overview of other autoimmune conditions, visit our Autoimmune Diseases page.