Table of Contents
Definition
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS) is a rare, rapidly progressive autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nervous system. This condition can cause muscle weakness, paralysis, and various sensory disturbances. GBS can affect individuals of any age and is often triggered by an infection, such as a respiratory or gastrointestinal viral infection.
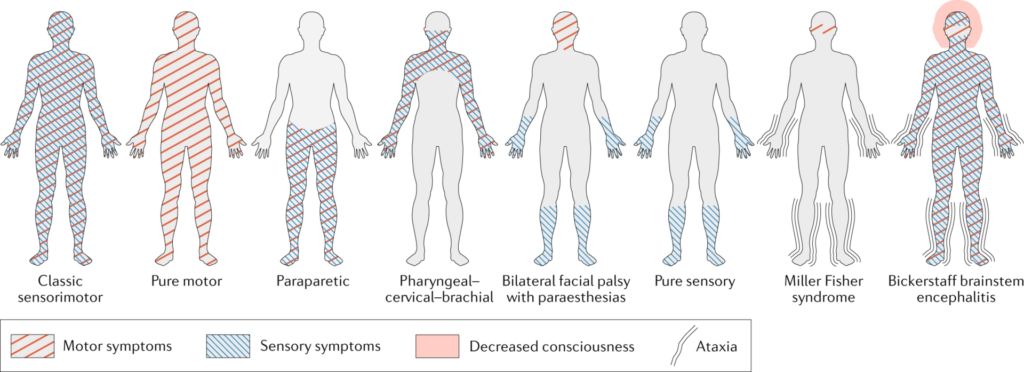
Symptoms
The symptoms of GBS typically develop rapidly over a few days to weeks and can vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Muscle Weakness: Begins in the legs and spreads to the upper body and arms.
- Tingling and Numbness: Sensations of pins and needles, usually starting in the feet and hands.
- Loss of Reflexes: Reduced or absent reflexes, such as knee-jerk.
- Difficulty Walking: Unsteady gait and difficulty climbing stairs.
- Paralysis: Severe cases may lead to total paralysis.
- Difficulty with Eye or Facial Movements: Trouble moving the eyes, blinking, or smiling.
- Severe Pain: Aching, cramping, or shooting pain, particularly at night.
- Breathing Difficulties: Weakness of respiratory muscles, potentially requiring ventilatory support.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rate.
When to See a Doctor
Immediate medical attention is crucial for Guillain-Barré Syndrome due to its rapid progression and potential severity. You should see a doctor if you experience:
- Rapidly worsening muscle weakness.
- Tingling and numbness that spreads quickly.
- Difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking.
- Severe pain or changes in heart rate and blood pressure.
- Difficulty with eye or facial movements.
Causes
The exact cause of Guillain-Barré Syndrome is unknown, but it is believed to result from an immune response that mistakenly targets the peripheral nerves. Potential contributing factors include:
- Infections: Most commonly associated with respiratory or gastrointestinal infections, such as Campylobacter jejuni, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, and Zika virus.
- Vaccinations: In rare cases, certain vaccinations may trigger Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
- Surgery or Trauma: Physical trauma or surgical procedures can sometimes precede GBS.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing Guillain-Barré Syndrome, including:
- Infections: Recent bacterial or viral infections.
- Age: More common in adults and older individuals.
- Sex: Slightly more prevalent in men.
- Autoimmune Disorders: History of other autoimmune diseases may increase the risk.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing GBS involves several steps:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: The doctor will review symptoms and perform a thorough neurological examination.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): To check for elevated protein levels in cerebrospinal fluid, which is common in Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
- Electromyography (EMG): To measure the electrical activity of muscles and assess nerve function.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: To evaluate the speed and strength of electrical signals in the nerves.
Treatment Approaches
There is no cure for Guillain-Barré Syndrome, but various treatment options can help manage symptoms, reduce the duration of the illness, and support recovery. Treatment approaches include:
- Plasma Exchange (Plasmapheresis):
- Plasmapheresis: To remove antibodies from the blood that are attacking the nerves.
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG):
- IVIG: High doses of immunoglobulins are given to block the damaging antibodies.
- Medications:
- Pain Relievers: To manage severe pain.
- Anticoagulants: To prevent blood clots due to immobility.
- Supportive Care:
- Respiratory Support: Mechanical ventilation if breathing is severely affected.
- Physical Therapy: To improve muscle strength and prevent contractures.
- Occupational Therapy: To assist with daily activities and adaptations.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, several lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage Guillain-Barré Syndrome symptoms and support recovery:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet to support overall health and recovery.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers to monitor progress and adjust treatments as needed.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing to manage stress.
- Gradual Exercise: Engaging in gentle physical activity as recommended by a healthcare provider to regain strength.
Complications
Guillain-Barré Syndrome can lead to several complications if not properly managed, including:
- Respiratory Failure: Due to weakness of respiratory muscles.
- Prolonged Paralysis: Persistent weakness or paralysis.
- Blood Clots: Increased risk due to immobility.
- Pressure Sores: Due to prolonged bed rest.
- Chronic Pain: Persistent nerve pain.
Recent Updates
Recent advancements in Guillain-Barré Syndrome research include:
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: Development of more precise tests to diagnose GBS earlier and more accurately.
- Genetic Research: Identifying genetic markers to better understand susceptibility to Guillain-Barré Syndrome and develop personalized treatments.
- New Treatment Options: Exploring new immunotherapies and medications to treat GBS more effectively.
- Rehabilitation Techniques: Enhanced physical and occupational therapy approaches to improve recovery outcomes.
Conclusion
Managing Guillain-Barré Syndrome effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and regular consultations with healthcare providers. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in preventing complications and improving recovery outcomes. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options can empower individuals to better manage their condition and maintain a good quality of life. If you experience persistent or rapidly worsening symptoms of GBS, seek immediate medical attention for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management.
Additional Content
For comprehensive information on the various treatments you can explore our Autoimmune Disease Treatment page. If you are seeking expert medical advice, our Top Autoimmune Doctors section provides a list of highly recommended specialists. Additionally, for an overview of other autoimmune conditions, visit our Autoimmune Diseases page.