Table of Contents
Dermatomyositis: Symptoms, Causes & Effective Management
This is a rare inflammatory disease characterized by distinctive skin rashes and progressive muscle weakness. It belongs to a group of muscle disorders known as inflammatory myopathies and can significantly impact physical health, daily activities, and quality of life.
Quick Facts
- Prevalence: Approximately 1-10 cases per million people globally.
- Common Symptoms: Muscle weakness, skin rashes, fatigue.
- Affected Population: Can occur at any age but commonly affects adults aged 40-60 and children aged 5-15, with a higher incidence in women.
Understanding Dermatomyositis
This disease involves inflammation in the muscles and skin, caused by autoimmune mechanisms. The immune system mistakenly targets muscle tissue and blood vessels in the skin, leading to distinctive rashes, muscle weakness, and potential organ involvement.
Common Symptoms
Early recognition and intervention significantly improve management and outcomes:
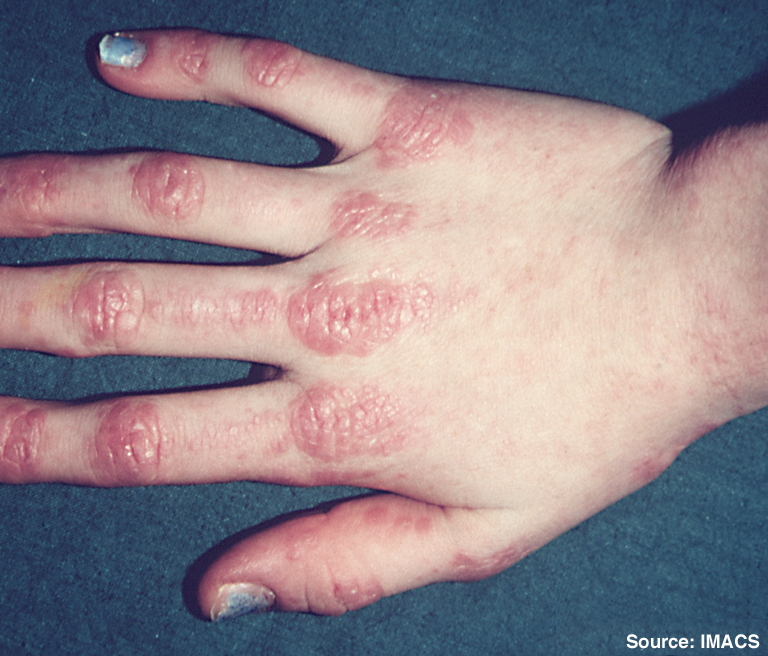
- Distinctive skin rashes, typically appearing as a violet-colored rash on the eyelids (heliotrope rash) or knuckles, elbows, knees (Gottron’s papules)
- Progressive muscle weakness, especially in the shoulders, hips, neck, and upper arms
- Difficulty climbing stairs, rising from seated positions, or lifting objects
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Muscle tenderness or pain
- Shortness of breath if lung involvement occurs
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of this autoimmune condition is unclear, but several factors have been identified:
- Autoimmune Response: Immune system mistakenly attacking muscle and skin tissues.
- Genetic Factors: Family history of autoimmune disorders may increase risk.
- Environmental Triggers: Potential triggers include viral infections, sun exposure, certain medications, and underlying malignancies in adults.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing this disease involves several assessments:
- Medical History: Comprehensive review of symptoms, their progression, and family medical background.
- Physical Examination: Assessing muscle strength, skin rashes, and signs of internal organ involvement.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to detect muscle enzyme elevations (CK, aldolase), inflammation markers, and autoantibodies (ANA, Anti-Jo-1).
- Imaging Studies: MRI to detect muscle inflammation and electromyography (EMG) to evaluate muscle activity.
- Muscle Biopsy: Confirmatory test revealing characteristic inflammation and muscle fiber damage.
Effective Treatments and Management
While there is currently no cure, effective treatments manage symptoms, control inflammation, and prevent complications:
- Medication: Corticosteroids as first-line treatment, immunosuppressants, biologics, and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG).
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: Strengthening muscles, preserving function, improving daily life activities.
- Skin Protection: Regular use of sunscreen, protective clothing, and topical treatments to manage rashes.
- Regular Monitoring: Routine medical check-ups to monitor treatment response and detect potential complications early.
Potential Complications if Left Untreated
Untreated or poorly managed this condition can lead to serious complications:
- Severe muscle wasting and loss of mobility
- Lung complications such as interstitial lung disease
- Difficulty swallowing, increasing risk of aspiration pneumonia
- Increased risk of malignancies, particularly in adult patients
- Chronic skin changes and potential infections
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if experiencing persistent muscle weakness, distinctive skin rashes, fatigue, or difficulty swallowing. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can greatly enhance outcomes and quality of life.
Practical Tips for Living with Dermatomyositis
Effective daily management strategies include:
- Consistent adherence to prescribed medications and therapies.
- Engaging in regular, supervised physical activity tailored to your capabilities.
- Protecting skin from sun exposure to minimize flare-ups.
- Incorporating a balanced diet and hydration to maintain overall health and muscle function.
- Utilizing stress management techniques like mindfulness or yoga.
- Connecting with support groups for emotional encouragement, practical advice, and sharing experiences.
Recent Research and Advances
Current research continues to enhance understanding and management of this disease:
- Development of novel therapeutic agents targeting specific immune pathways.
- Advancements in diagnostic techniques, including imaging and autoantibody profiling.
- Studies investigating genetic and environmental factors contributing to disease development.
- Exploration of personalized treatments to improve patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it hereditary? While this autoimmune condition is not directly hereditary, genetic predispositions may increase susceptibility to autoimmune diseases.
Can dermatomyositis be cured? Currently, no cure exists, but early diagnosis and effective management significantly control symptoms and prevent complications.
Does dermatomyositis affect life expectancy? Life expectancy can be normal or near-normal with appropriate treatment and management, although severe complications, if untreated, can affect outcomes.
Additional Content
For comprehensive information on the various treatments you can explore our Autoimmune Disease Treatment page. If you are seeking expert medical advice, our Top Autoimmune Doctors section provides a list of highly recommended specialists. Additionally, for an overview of other autoimmune conditions, visit our Autoimmune Diseases page.