Table of Contents
Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH): Symptoms, Causes & Effective Management
Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic liver inflammation caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking liver cells. If untreated, AIH can lead to serious liver damage, affecting overall health and quality of life.
Quick Facts
- Prevalence: Approximately 10-17 cases per 100,000 people globally.
- Common Symptoms: Fatigue, jaundice, abdominal discomfort.
- Affected Population: Predominantly affects women, commonly diagnosed between ages 15-40, though it can occur at any age.
Understanding Autoimmune Hepatitis
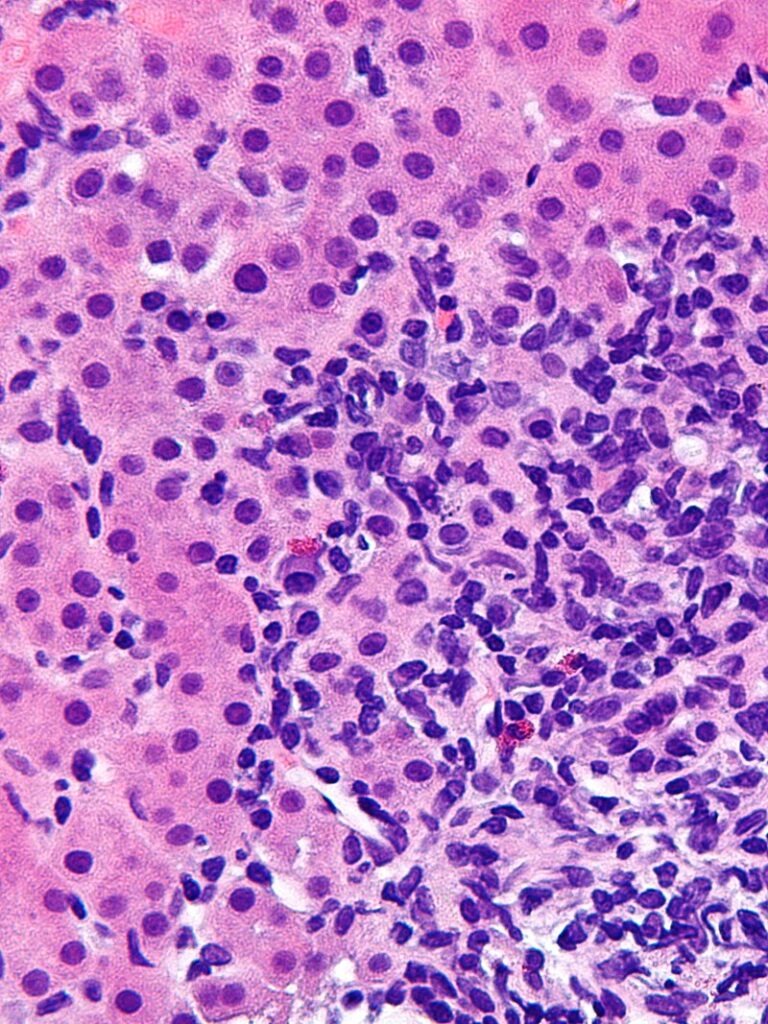
AIH occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly identifies liver cells as foreign, leading to chronic inflammation and progressive liver damage. Over time, this immune-mediated damage can result in scarring (cirrhosis), liver failure, and increased risk of liver cancer.
Common Symptoms
Early detection and timely treatment improve outcomes significantly:
- Chronic fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal discomfort or swelling
- Joint pain or arthritis-like symptoms
- Loss of appetite and unintended weight loss
- Dark urine and pale-colored stools
- Nausea or vomiting
- Skin rashes or itching
Symptoms vary widely among individuals, and some may initially experience minimal or no symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of AIH is unknown, but several contributing factors are recognized:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of autoimmune conditions increases risk.
- Environmental Triggers: Potential factors include viral infections, medications, or toxins.
- Autoimmune Association: Increased likelihood of developing AIH with existing autoimmune diseases like thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, or inflammatory bowel disease.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing autoimmune hepatitis typically involves:
- Medical History: Thorough evaluation of symptoms, personal medical history, and family background.
- Physical Examination: Checking for jaundice, liver enlargement, or signs of liver disease.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests for liver enzyme elevations (ALT, AST), autoantibodies (ANA, ASMA), and immunoglobulin G levels.
- Liver Biopsy: Essential to confirm diagnosis, assess severity, and determine appropriate treatment.
Effective Treatments and Management
While there is no cure, effective treatments can manage inflammation, prevent liver damage, and improve quality of life:
- Medication: Immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids and azathioprine to control inflammation and immune response.
- Regular Monitoring: Routine blood tests and medical visits to monitor liver function and treatment effectiveness.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoiding alcohol, maintaining a healthy diet, and regular exercise.
- Liver Transplantation: Considered in severe cases or when significant liver damage occurs.
Potential Complications if Left Untreated
If untreated, AIH can lead to serious complications:
- Liver cirrhosis (permanent scarring)
- Liver failure, potentially requiring transplantation
- Increased risk of liver cancer
- Complications from portal hypertension (e.g., bleeding from esophageal varices)
When to See a Doctor
Consult your healthcare provider if experiencing persistent fatigue, jaundice, abdominal discomfort, or other concerning symptoms. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are critical to managing AIH and preventing severe complications.
Practical Tips for Living with Autoimmune Hepatitis
Effective daily management includes:
- Strict adherence to medication regimens and medical appointments.
- Maintaining a nutritious diet, avoiding alcohol, and limiting liver-stressing substances.
- Engaging in regular, moderate exercise to support overall health.
- Utilizing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or mindfulness.
- Joining support groups to connect with others, share experiences, and obtain emotional support.
Recent Research and Advances
Ongoing research continues to enhance the understanding and management of autoimmune hepatitis:
- Studies exploring genetic and environmental interactions in disease development.
- Development of targeted therapies with improved efficacy and fewer side effects.
- Advances in non-invasive diagnostic and monitoring techniques.
- Investigations into personalized treatment strategies based on genetic and clinical profiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is autoimmune hepatitis hereditary? While not directly inherited, having family members with autoimmune conditions may increase susceptibility.
Can autoimmune hepatitis be cured? Currently, AIH has no cure, but treatment can effectively manage symptoms and prevent severe liver damage.
Does autoimmune hepatitis affect life expectancy? With proper diagnosis and effective management, individuals with AIH can maintain normal or near-normal life expectancy.
Additional Content
For comprehensive information on the various treatments you can explore our Autoimmune Disease Treatment page. If you are seeking expert medical advice, our Top Autoimmune Doctors section provides a list of highly recommended specialists. Additionally, for an overview of other autoimmune conditions, visit our Autoimmune Diseases page.